
30 range, but interestingly enough it correlated decently with intelligence tests (1).Ī key difference between the Rorschach and the HIT was that participants taking the HIT were only allowed a single response per plate, where as the Rorschach was more open ended. Introduction The Rorschach test also known as the Rorschach inkblot test, the Rorschach technique, or simply the inkblot test is a psychological test in which subjects perceptions of inkblots are recorded and then analyzed using psychological interpretation, complex algorithms, or both. Inter-rater reliability was adequate, and test-retest reliability was found to be in the. Despite the HIT's attempt to overcome the psychometric problems associated with the Rorschach, it too suffered in low validity. In this monograph, we review the current state of the literature concerning the psychometric properties (norms, reliability, validity, incremental validity, treatment utility) of three major projective instruments: Rorschach Inkblot Test, Thematic Apperception Test (TAT), and human figure drawings. It was first introduced in 1961 as a projective personality test similar to the Rorschach.The HIT is a standardized measurement. Number of inkblots: While the traditional Rorschach test has ten inkblots, the Holtzman Inkblot Technique has forty-five blots, and two practice cards (Holtzman, 1968, p. The HIT was designed to address the problems associated with the Rorschach Inkblot Technique, such as inadequate standardized scoring and issues with psychometrics. The Holtzman inkblot technique (HIT), also known as the Holtzman inkblot test, is an ink blot test aimed at detecting personality and was conceived by Wayne H. Scoring of the assessment was based on 22 items: reaction time, rejection, location, space, form definiteness, form appropriateness, color, shading, movement, pathognomonic verbalization, integration, content (human, animal, sexual, anatomy, abstract), anxiety, hostility, barrier, balance, popularity, and penetration. It was administered individually, but could be used to study whole groups as normed data was present in the manual. The Rorschach test is a projective psychological test in which subjects perceptions of inkblots are recorded and then analyzed using psychological.

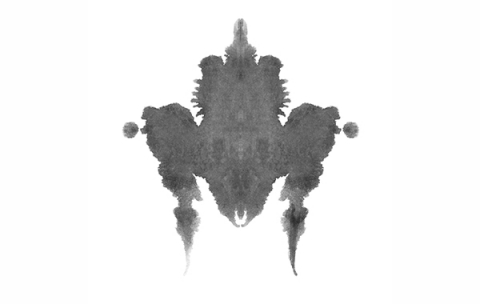
The present article identifies problems with the Rorschach regarding norms, cultural sensitivity, interrater reliability, test-retest reliability, validity, factor structure, and accessibility of supporting studies. The Holtzman Inkblot Technique was a projective personality assessment containing 45 inkblot plates. Over half a century later, overstatements regarding the test are still common. Randolph College Psychology Collection Name/Title 1958) firstly proposed a valid and reliable content-analysis scoring system of body boundary awareness based on verbal responses of Rorschach inkblot tests.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
